There are three basic parts of the brain. The Hindbrain, Inner Brain, and Forebrain. The forebrain is broken down into four major lobes. Naturally everything can be broken down further but lets get started with the basics.
Please note I am not a doctor. Refer to resources for more information about different parts of brain anatomy.
Forebrain
Frontal Lobe
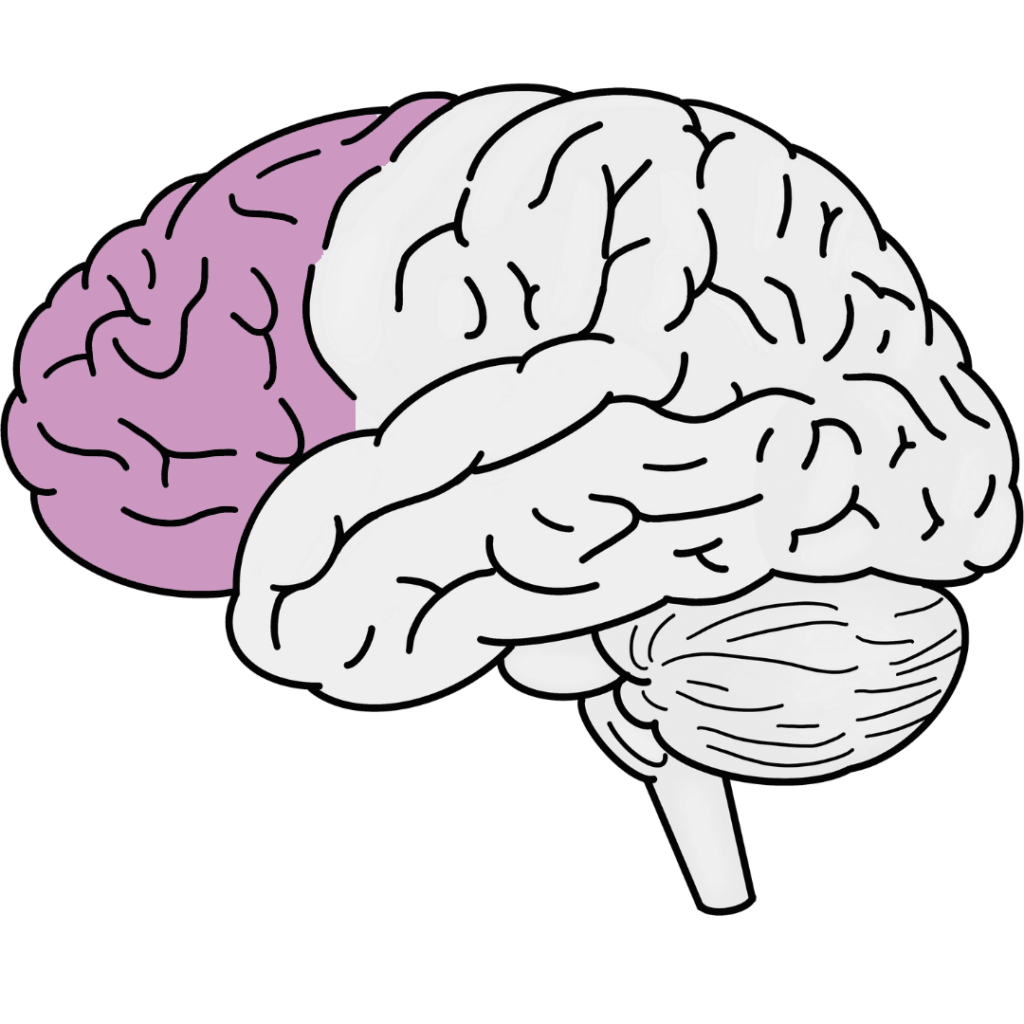
Located at the front of the brain, the frontal lobe is involved in decision-making, problem-solving, planning, reasoning, and voluntary muscle movements. It also influences aspects of our personality and social behavior.
Parietal Lobe
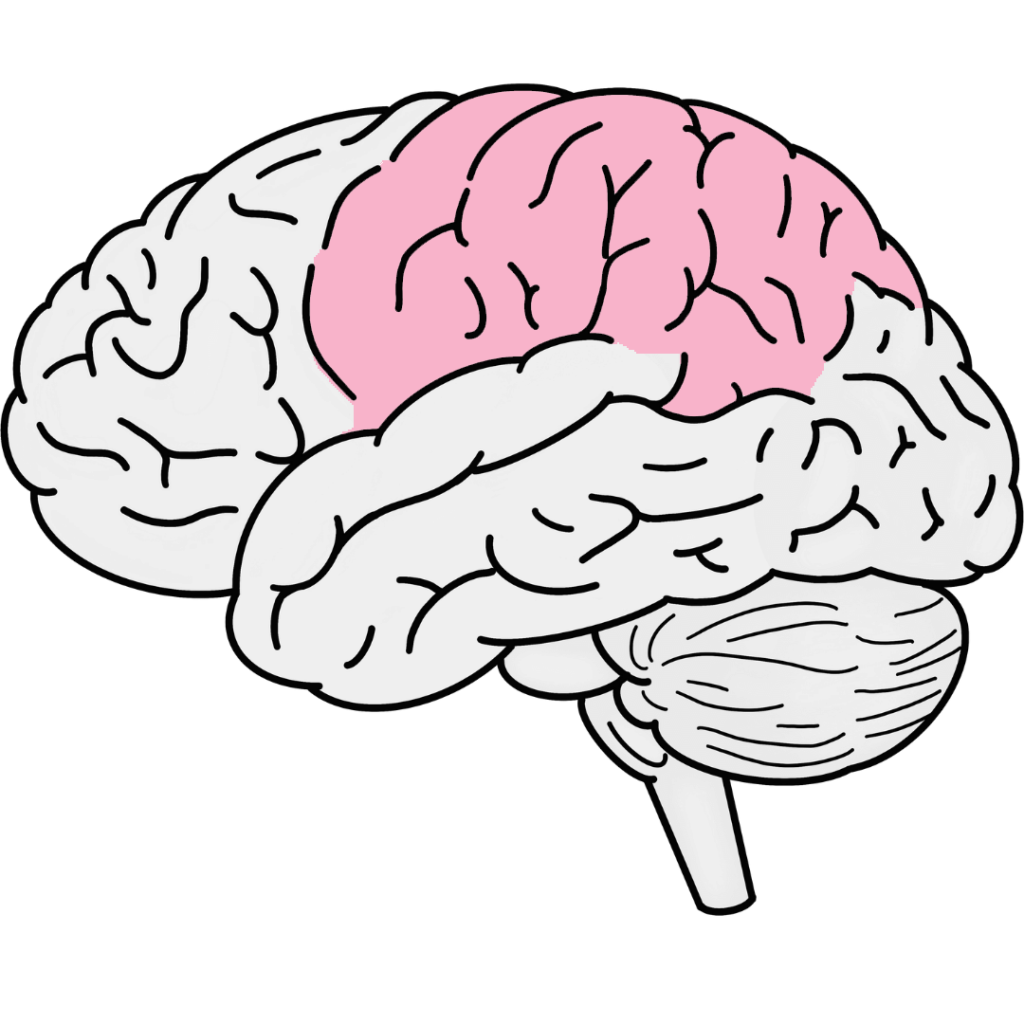
Positioned in the middle of the brain, the parietal lobe is responsible for processing sensory information from the body, such as touch, temperature, and spatial awareness. It helps us navigate our environment and interact with it effectively.
Occipital Lobe
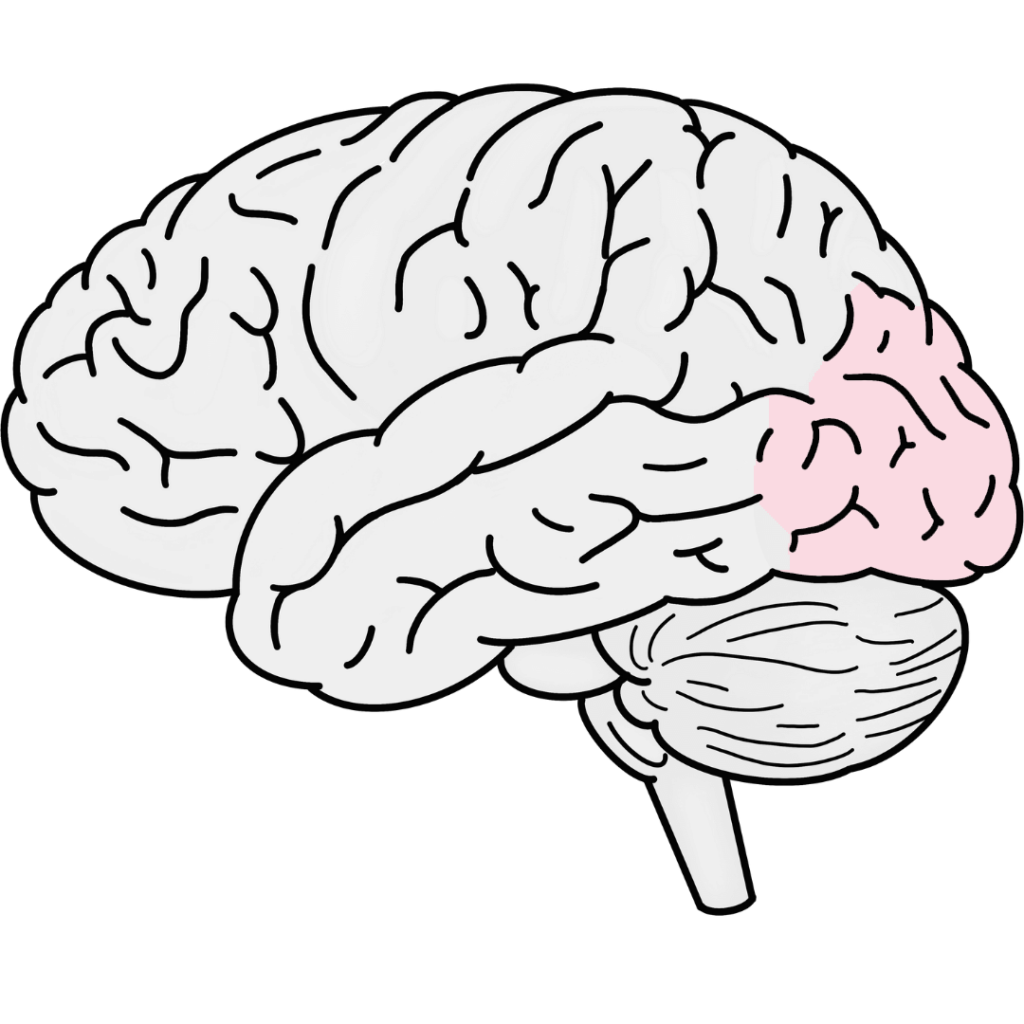
Situated at the back of the brain, the occipital lobe primarily handles visual processing. It allows us to interpret and understand visual information received from the eyes.
Temporal Lobe
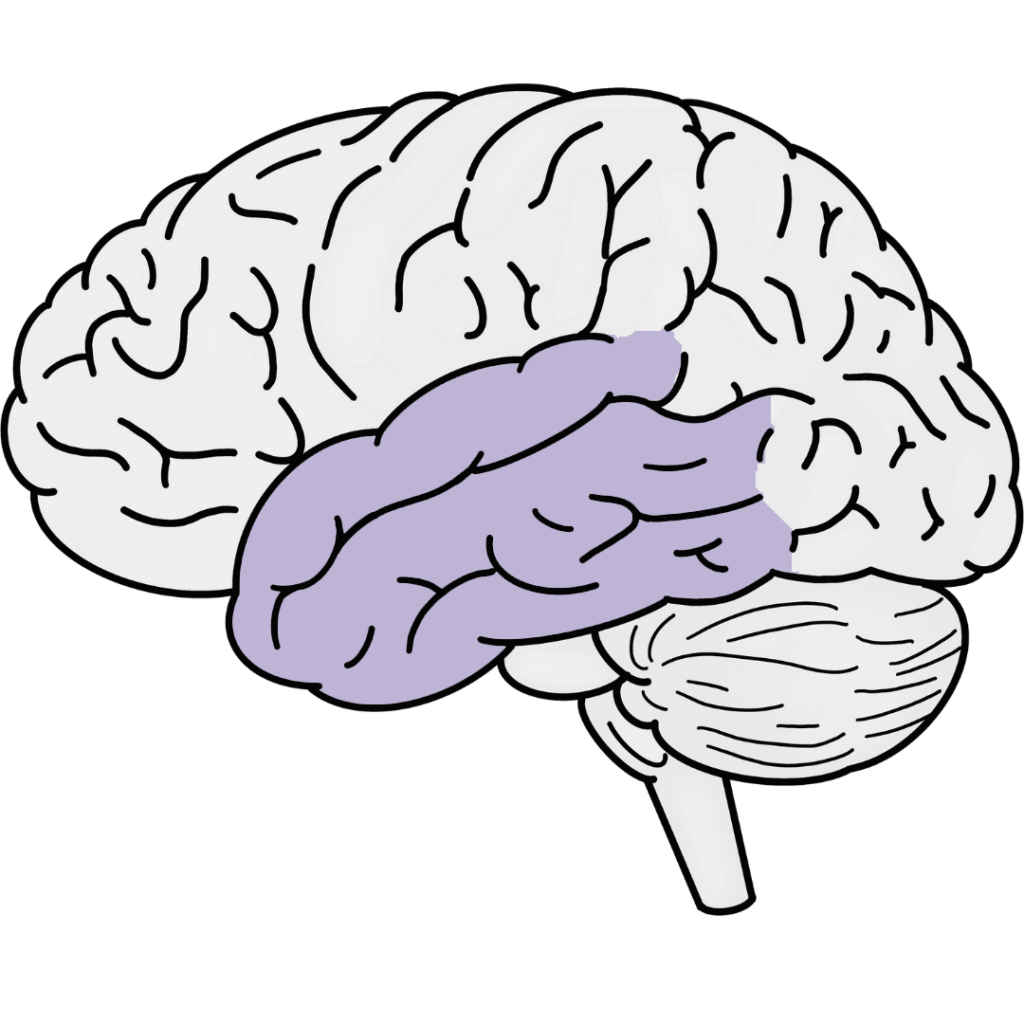
Found on the sides of the brain, near the temples, the temporal lobe is vital for auditory processing and language comprehension. It is also involved in memory formation and emotional regulation. I am particularly interested in the effects of the temporal lobe as it was the portion that has scar tissue after my Traumatic Brain Injury. Click here to learn more about my TBI.
Within the temporal lobe, the hippocampus (pictured below) plays a crucial role in forming and consolidating memories. It is essential for learning and memory processes.
Also located in the temporal lobe, the amygdala (not pictured) is involved in processing emotions, particularly fear and aggression. It plays a role in emotional responses and emotional memory formation.
Hindbrain
Cerebellum
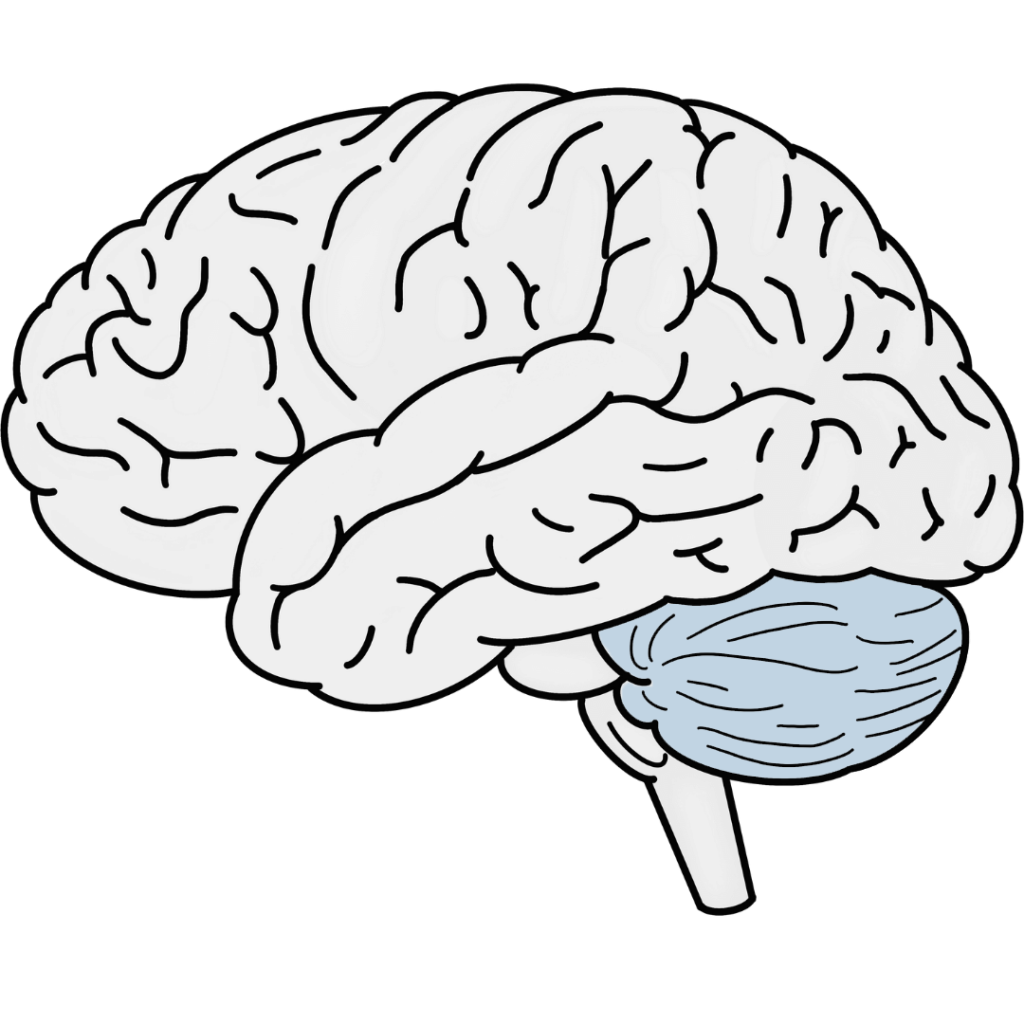
Located under the cerebrum at the back of the brain, the cerebellum is responsible for coordinating movement, balance, and posture. It enables precise and smooth execution of voluntary movements.
Brainstem
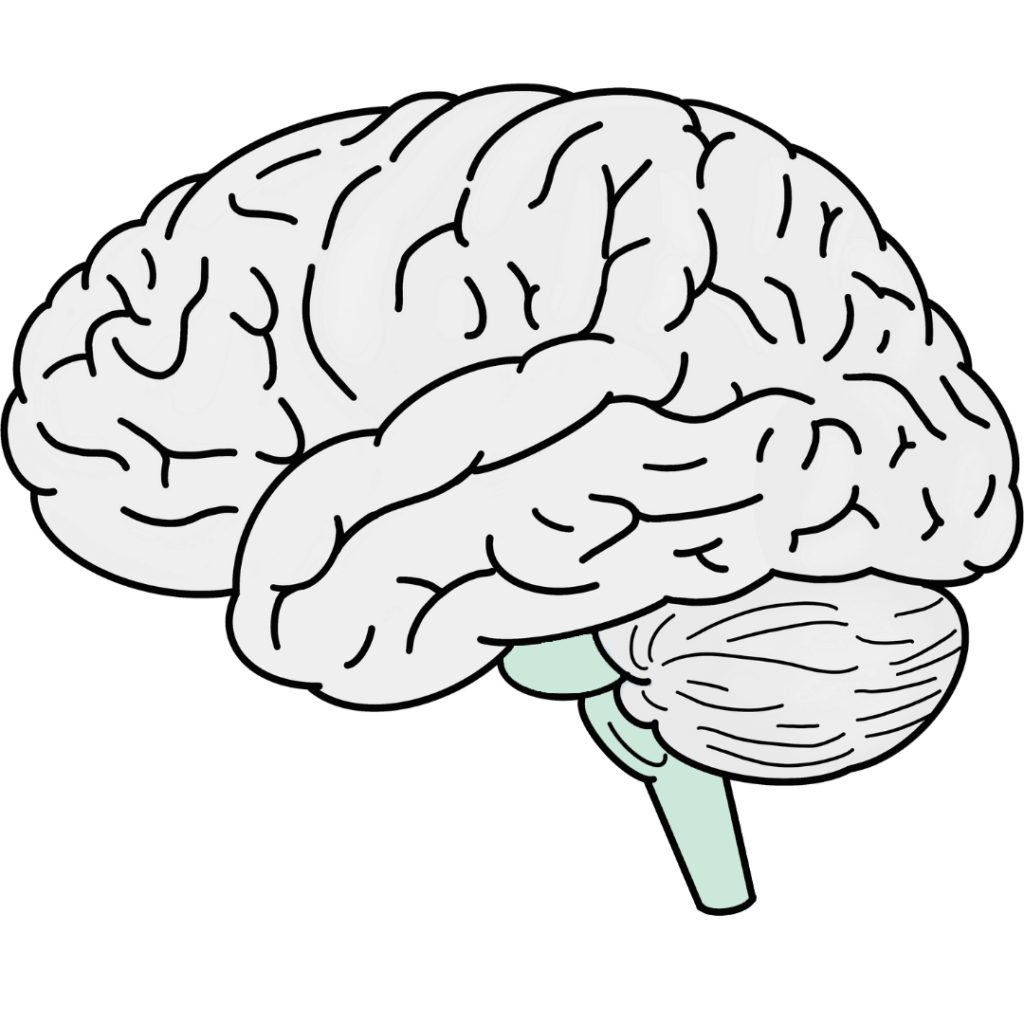
The brainstem is a critical structure that connects the brain to the spinal cord. It consists of the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata. The brainstem controls essential functions like breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, and digestion.
Inner Brain
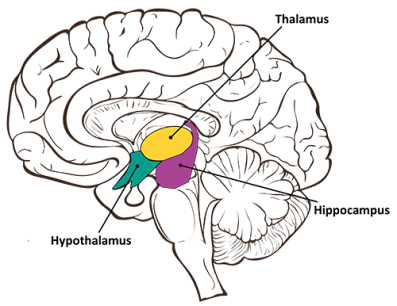
Thalamus
The thalamus serves as a relay center for sensory information, routing it to the appropriate areas of the cerebral cortex for further processing. It is involved in sensory perception, motor control, and attention.
Hypothalamus
Situated below the thalamus, the hypothalamus regulates various homeostatic processes, including body temperature, hunger, thirst, and sleep-wake cycles. It also controls the release of hormones by the pituitary gland.
Basal Ganglia (not pictured)
This group of nuclei is located deep within the cerebral hemispheres. The basal ganglia are crucial for motor control, procedural learning, habit formation, and emotion regulation.
Anatomy is a fascinating subject that gets more and more in depth the further in you go. Brain anatomy is more vast than what this touched on but learning the basics is a great way to get started with this subject.
Grow your brain with knowledge!
Rachel McG

- NIH Public education “Brain basics: Know your Brain” Click here for the link
- Ackerman S. Discovering the Brain. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 1992. 2, Major Structures and Functions of the Brain. Available from: Click here for the link.
- Maldonado KA, Alsayouri K. Physiology, Brain. [Updated 2023 Mar 17]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: Click here for the link.
- Patel A, Biso GMNR, Fowler JB. Neuroanatomy, Temporal Lobe. [Updated 2022 Jul 25]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: Click here for the link to this study.